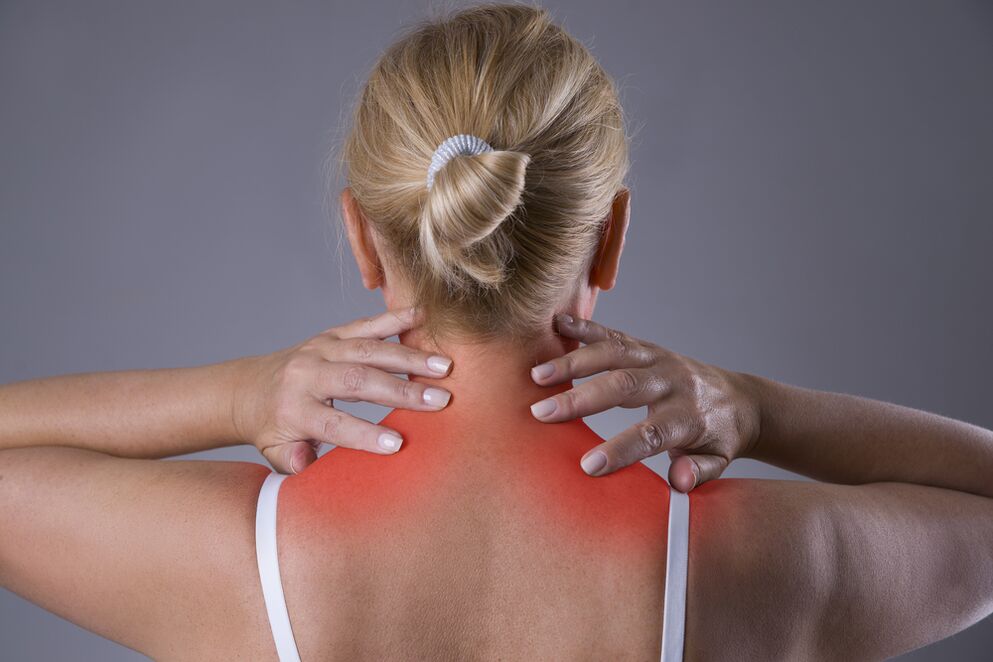
Why is osteochondrosis dangerous?
- The dense annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc is destroyed and cracks appear in it.
- The contour of the disc moves beyond physiological boundaries, forming a herniation
- Without expert help from the previous stage, the patient will face annulus fibrosus rupture and hernia
- Osteophytes form on cartilage and bone tissue - pathological growths that become one of the causes of reduced mobility and pain in the spine.
- Compression and inflammation of the spinal cord roots and surrounding tissues
Undiscussed characteristics of cervical osteochondrosis
What threatens the development of cervical osteochondrosis?
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
- Spasticity and restriction of neck movement, pain when turning and tilting the head
- Burning sensation, soreness, foreign body sensation in throat, difficulty swallowing
- Numbness and coldness in the hands or only the fingers
- Chest pain and burning sensation
- lack of air
- chronic hypertension
- Headache, migraine
- dizziness, fainting
- Noise and tinnitus
- Decreased vision and spots appearing in front of the eyes
- Increased fatigue, weakness, lethargy, decreased performance
- Difficulty concentrating and forgetfulness
- sleep disorder
- chronic depression
- panic attack
- Pain of varying intensity that spreads to the neck, shoulders, collarbone, upper back, and the entire surface of the head from the back of the head to the forehead
Clinical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in men and women
Preventing the development of cervical osteochondrosis
- Take long walks every day. In total, you need to take at least 6, 000 steps per day.
- do excercise. The load should not be too large. Start with feasible exercises and gradually increase the duration and number of repetitions of the exercises.
- Eat a balanced diet and maintain a normal weight.
- Perform Dr. Shishonin's neck exercises.